Push Notifications Explained
A push notification is an alert generated by a mobile phone app, when the app isn’t open, that pops up to alert the user to a new message, update or promotional offer. Depending on the type of app, a typical message distributed via a push notification can be a news flash alert, a sports score, an invitation to a flash sale or a boarding gate announcement, just to name a few examples. App publishers can send them at any time, even when the app isn’t open, since users don’t have to be in the app or using their devices to receive them. All the mobile platforms — iOS, Android, and Fire OS — have their own services for supporting push, and any app can send these mobile push notifications to those who have the app installed and push enabled.
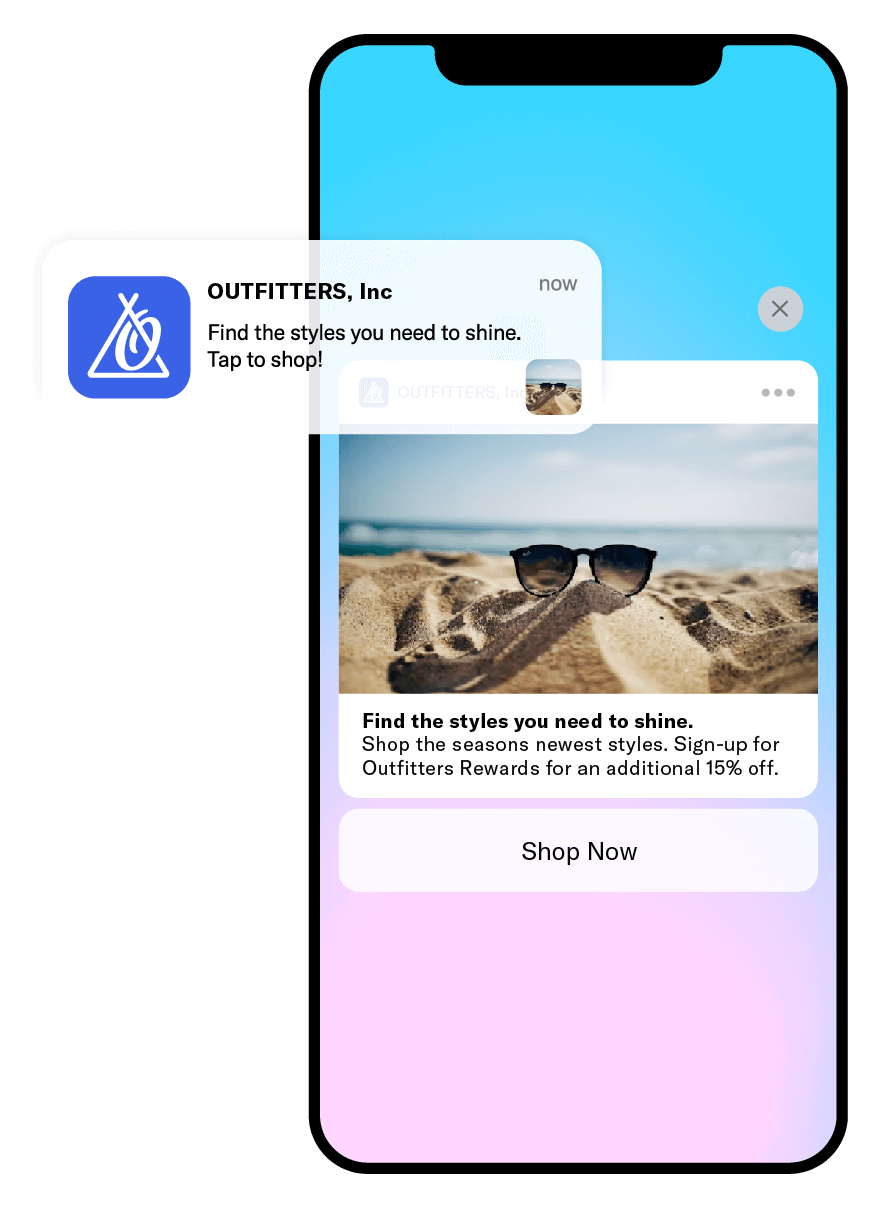
What Do Push Notifications Look Like?
- A bolded title with some context about the notification’s content
- A time stamp to show when the notification was sent
- A few sentences of text in the message body offering more information
- The app icon to let the user know where the notification is coming from
They can also include:
- Buttons with a call to action, e.g. “Buy Now,” “Follow” or “Share”
- A thumbnail of an media attached to the push notification, visible in full size when the notification is expanded (this can be an image, an animated gif or a video (iOS only))
How Do Push Notifications Appear To Users?
Users typically see a notification as a banner or pop-up alert as they use their phones. The alert appears no matter what the user is doing. Most mobile operating systems also show push notifications together in a single view.
- On iOS, Apple’s Notification Center is organized in chronological order. Users can choose to see a List or Stack notifications, where unopened push notifications from the same app are all nested under the most recent one. Users access the Notification Center by swiping down from the top of the screen. iOS lets users customize push notifications at an individual app level; users can turn sounds on or off and pick the notification styles they do or don’t want from each app (Lock Screen, Notification Centre and Banners). Since the introduction of Time-Sensitive Notifications, users have the option to receive push notifications from specific apps that are deemed time-sensitive by the apps, even if the device is in Focus Mode or a similar setting. This feature ensures that critical notifications can still reach users when necessary, even if they have chosen to limit distractions through Focus Mode. Lastly, users can also control the red “badge” showing the number of unread notifications inside an app on the home screen icon of the app.
- On Android, devices show unread messages on the lock screen. Android uses a standard banner approach that users cannot change at an OS level, though they can customize the notification sound and whether a notification dot appears on the app icon, alerting the user to a new notification. Users can choose per app whether to get all push notifications, none at all, or only Sensitive Notifications. They can also choose to ‘snooze’ push notifications from a specific app for a set period of time.
What Are The Different Types of Push Notifications?
Push notifications can serve a lot of different purposes and often fall into one of these categories:
Transactional
Transactional push notifications are triggered by an action a user takes in an app, such as completing a purchase, resetting a password, making a payment, abandoning a cart or registering for an event. These types of notifications are important confirmations for users, as they provide important updates on deliveries, payments, appointment confirmations and more. They make the app experience better for consumers by confirming their action was registered correctly.
Marketing
Promotional app notifications generate interest in a company’s services, products or events to bring people further down the marketing funnel and ultimately increase sales or engagement. Businesses may use promotional notifications to announce a product launch, a sales promotion, a loyalty reward or even a personalized recommendation based on past behaviors or preferences.
Informational
Informational notifications simply provide helpful updates and information rather than requiring the user to take action. Examples include breaking news alerts from news apps, flight status updates from airline apps, system updates from technology and service apps or changing weather conditions from a weather app.
Reminders
These helpful alerts bring a deadline or commitment to the front of a user’s mind, such as a task, action, or event they need to take. These types of notifications are common with fitness, financial, educational, medical and calendar apps, providing reminders about a person’s morning walk not being logged, a project or bill being past due, a morning medication needing to be taken or an upcoming dental appointment. Duolingo is one such app that pops in every day to remind people to stay consistent with their daily language study.
Geolocation-based
When users enable location services and give an app permission to track their location, the app can send them relevant messages based on where they are, such as local traffic conditions or sales at a nearby department store. It sets up geofences so that when the user enters or exits specific areas, automated notifications will be triggered. For example, if a consumer frequents a specific Starbucks location, the Starbucks app may invite them to pop in for their regular vanilla latte when they’re nearby. Dating apps are another good example, as they may alert you about how many singles with the app are within a few miles of your location.
Why are Push Notifications Used?
For app publishers, push notifications are a way to speak directly to the user instead of getting caught in spam filters or forgotten in an inbox. As a result, push click-through rates can be twice as high as email. They can remind users to use an app, even if it isn’t open, and serve various purposes:
- Promoting products or offers to increase sales
- Improving customer experience
- Converting unknown app users to known customers
- Sending transactional receipts right away
- Driving users to other marketing channels, such as social networks
6 Advantages of Using Push Notifications
Here are six advantages of using push notifications to keep your app top of mind and enhance overall engagement and business growth.
- Engage and retain customers: With the sheer number of apps available for download and the many uses for a smartphone, it’s common for users to forget about an app once they’ve downloaded it. A simple push notification, however, can keep people engaged and active. App users who receive any push notifications in their first 90-days have 3X higher app retention rate when compared to those who received no push notifications.
- Boost revenue through upsells/cross-sells: Based on current cart items or previous clicks and purchases, apps can suggest additional or premium products that will complement what they purchased or are very similar to the customer’s interests. For example, a consumer purchasing a laptop could be sent a push notification offering a protection plan (upsell) or a protective sleeve (cross-sell) for the computer. By suggesting higher-end items or additional products to complement a purchase, a business can increase its average order value and total revenue.
- Enable audience segmentation: Not all push notifications will have the same appeal to every customer. Fortunately, with push notifications as a natural extension of your customer engagement platform (CEP), businesses can segment groups based on shared data and characteristics, using this to customize offers and messaging to each individual’s needs.
- Increase conversions: Real-time marketing offers through push notifications are a great way to bring customers to a purchase. When you introduce limited-time offers like flash sales, you create a sense of urgency around your products and services that urges them to buy sooner rather than later. Push notifications are also a proven way to increase conversion by sending users back into the purchase funnel after they abandoned it, for example through an abandon cart / abandon basket campaign.
- Improve communication: Throughout the customer lifecycle, from onboarding and regular usage to potential churn, notifications can provide relevant information and reminders. This helps maintain a continuous dialogue with the user and enhances their journey with timely, useful touchpoints that encourage loyalty and sustained engagement.
- Create a seamless user experience: Push notifications can integrate with other customer touchpoints to support in-app and website interactions, email and social campaigns and more for a cohesive experience. Using data on a user’s behavior, location and preferences can help a business deliver helpful, real-time updates that fit seamlessly into their daily usage patterns and activities. This ensures the app remains a relevant and regular part of their digital customer experience.
Industries That Use Push Notifications
Push notifications can be useful for any industry, but some sectors use them more than others due to their ongoing need for real-time, actionable engagement and communication with users. These industries include:
- Retail and e-commerce: Retailers commonly use push notifications to send order delivery updates, promote sales, new product announcements, personalized promotions, time-sensitive offers, cart abandonment reminders and more based on a person’s purchase and browsing history.
- News and media: Push notifications are particularly useful for news and media apps, as they deliver news about important events in real-time, even when users are not actively using the app.
- Social media: Social media platforms use push notifications for messages, friend requests, trending content, post engagement and other interactions, which users can customize to their liking.
- Finance and banking: Banking apps allow users to receive real-time alerts about security notices, transactions, spending habits, stocks and more to enable more effective money management.
- Gaming: Gaming apps often use push notifications to promote new game features, invite players back after inactivity, send streak reminders, incentivize purchases and engagement, encourage engagement with other players and more.
- Education: These app types are known to use push notifications to make course announcements, encourage daily learning, alert students about graded assignments, remind them about upcoming due dates and make the learning experience more convenient.
- Hospitality and travel: When you download a hotel or airline app, you can get real-time push notifications about your flight status, itinerary, check-in times, promotional offers and communicate with customer service agents when you need assistance.
- Health and fitness: Fitness, fasting, calorie counting, and similar apps will send helpful push notifications reminding you to drink water, stand up, get your steps in, track your meals and check in with your body.
History
Push notifications have been around longer than you may think. Here’s a brief timeline of their development:
- June 2009: Apple launches Apple Push Notification Service (APNs), the first push service. Airship was the first company in the world to send a commercial push notification.
- May 2010: Google released its own service, Google Cloud to Device Messaging (C2DM).
- May 2013: Google introduces “rich notifications.” Rich notifications can contain images and action buttons, which let users take immediate action from a notification. For example, the user can play a song, open the app or see more information.
- September 2014: Apple added interactive buttons, allowing users to send a response right away to the app publisher. Shortly after, Apple extended push notifications to the Apple Watch.
- September 2016: Apple adds support for rich notifications in iOS 10.
- August 2017: Google introduces notification grouping with Notification Categories and notification dots, similar to iOS badges, which alert a user to active notifications for an app.
- September 2018: Apple introduces several notification updates, including notification grouping, quiet notifications for a less intrusive experience and provisional authorization. These updates allow users to understand the value of notifications before opting in. Google introduces suggested notification muting in Android P.
- August 2021: Google adds support for notification snoozing, along with a redesigned notification UX.
- September 2021: Apple introduces focus modes for controlling how and when notifications arrive on a device and notification types for Passive & Time Sensitive notifications, paired with new interruption levels for notification delivery and notification summaries. Users can select apps to include in a cross-app notification roundup that can be scheduled for delivery at specific times throughout the day.
- August 2022: Google now requires users to opt into notifications on Android devices with Android 13.
- October 2022: Apple takes push notifications to the next level with Live Activities. App users can now stay up to date on sports scores, transportation and food deliveries with one glance at their lock screen, instead of receiving multiple notifications. Only Airship supports both Live Activities for iOS and Live Updates for Android.
How Do Push Notifications Work?
Some of the actors in sending a push notification include:
- Operating system push notification service (OSPNS). Each mobile operating system (OS), including iOS, Android, Fire OS and Windows, has its own service.
- App publisher. The app publisher enables its app with one or more OSPNSs and uploads the app to the app store.
- Client app. This is an OS-specific app installed on a user’s device. It receives incoming notifications.
Once the app is live on the app store and a user installs it on their device, it registers with the operating system’s push notification service — whether Apple APNs for iOS or Google FCM for Android. The app will get a unique identifier, which is sent to the app server. When the publisher wants to send a notification, they use their unique identifier to send a message to the push notification service, which is the service that delivers the message to the right devices. Users get the notifications in real-time, subject to their device settings and notification preferences for the app.
Push notifications can be targeted to segments of your user base and even personalized for specific app users. This requires managing user identification data and some kind of interface for writing, targeting and sending messages. This can be built in-house or bought as a SaaS solution, usually in the form of a Customer Engagement Platform (CEP), CRM system or Marketing Automation Platform.
User Activation
Here’s what happens after a user downloads an app:
- The user visits an OS app store, downloads the app and then installs it.
- The user opens the app. Unique identifiers (IDs) for both the app and the device are registered with the OSPNS.
- The IDs are passed back to the app from the OSPNS. They are also sent to the app publisher.
- The app publisher receives and stores these registration details, including the IDs.
Sending
In greater detail, here’s what happens when an app publisher is ready to send a push notification message:
- The app publisher composes a manual message through a message composer user interface. Alternatively, the publisher sets up an automated message to be sent via the API.
- The publisher defines the audience to whom the push notification will be sent.
- The publisher determines whether the message should be sent immediately or scheduled.
- The message is delivered to the OSPNS, and the OSPNS delivers the message to the user’s device as a push notification.
Opting In
Both iOS and Android requires apps to obtain permission from users before sending them push notifications. Historically, Android and Fire OS have not required user permission, but this changed with Android 13 in 2022. Convincing users to opt in has always been important for the success of apps on iOS and has proven to be so for be for Android as well.
The majority of apps show a standard system opt-in prompt when the app is first opened. A better approach is to show the value of opting in — for example, with a customized welcome series upon first open — and ask the user to opt in right after having shown them these benefits.
Based on Airship Benchmarks for 2024:
- The median push opt-in rate is 61.4% for Android vs 49.8% for iOS.
- Median opt-in rates for iOS range from 41.6% for Media apps to 76.8% for Education.
- Median opt-in rates for Android range from 49.1% for Social apps to 71.4% for Utility & Productivity apps.
- High-performing apps across all industry verticals and OSs (those in the 90th percentile) have opt-in rates above 63%.
Using Location with Push Notifications
All mobile operating systems ask users for their permission before sharing location information. When an app triggers a device location request, users are presented with the following options:
iOS:
- Allow once
- Allow while using the app
- Allow always (for background location requests)
- Don’t allow
Android:
- Allow only while using the app
- Allow all the time (for background location requests)
- Deny
- Ask every time (on some versions)
Brands can deliver more relevant messages by using location data combined with behavioral data. Examples include:
- A home improvement app sends offers for cooling units during a regional hot spell.
- A specialty boutique invites users within 50 miles of an invite-only VIP trunk sale.
- A national sporting goods chain invites local shoppers in for local pro athlete autographs.
For both Android and iOS, if the app requests precise location, the user is given the option to choose whether they’d like to share their ‘precise’ location, or only give ‘approximate’ location information instead. App publishers should consider whether approximate location will suffice for what they’re trying to achieve, and only as for precise location if it is essential. For example, in the case of fast food restaurants bringing out your order to your car, precise location is needed to see where exactly you’re parked.
Best Practices When Using Push Notifications
In order for push notifications to be effective, they need to be carefully planned and thought out. Here are a few best practices to keep in mind during the planning phase:
- Personalize notifications: By including the recipient’s name, relating to their previous actions and providing other individual details, you can improve the user experience and potentially improve app engagement.
- Consider the timing: Push notifications should be scheduled based on a user’s activity and the time zone they live in. The timing depends greatly on the app type, but try not to send them when the individual is likely to be sleeping or otherwise tends to be inactive. Airship makes this easy by giving you the option to automatically deliver pushes at a set local time, which is based on the app user’s device settings.
- Ensure relevance: A push notification that isn’t relevant to a user’s interests and behaviors is likely to be a waste. Use data from a CRM system, Customer Engagement Platform (CEP) or your other resources to create relevant, targeted messages for individuals.
- Use them sparingly: Constant push notifications can be annoying and lead users to ignore them, disable the notifications or even delete the app. Focus on quality notifications over quantity, as the average smartphone user gets 46 notifications or more daily and can easily become overloaded.
- Be clear and concise: Make sure users can understand what a push notification is about and what action it requires from them at first glance. A message body with up to 35 characters is ideal, and it should never have more than 147. Longer messages risk being cut off and have their ending replaced with ‘…’, making them more difficult to read for the user.
- Try A/B testing your messaging: Try out a few different messaging strategies for your audience segments to see which options work and which don’t. This provides information you can use to optimize future push notifications for best results.
- Incorporate rich media: Including visuals like GIFs, emojis, videos, or images can make your push notifications more memorable and eye-catching to the user, helping them stand out among other notifications they get on their phone. Use them sparingly, though, so they don’t come across as spam. Brands can create a powerful visual cue by consistently using a specific emoji for a specific type of message. Examples are a money emoji for transactional push notifications or truck emojis for delivery updates.
What Not To Do When Using Push Notifications
Now that we’ve discussed push notification best practices and what you should do, you should also be aware of the missteps to avoid when using these notifications.
- Don’t simply replace emails with push notifications: Some companies try to make their push notifications serve the same function as emails. Avoid using push for long-form messaging and use a combination of in-app messages, SMS, push notifications and emails instead. Rather than sending a very long push notification, brands can use them to link a user to longer-form content inside the app, e.g. in an app inbox.
- Don’t advertise other products or services: Advertising your other offerings beyond your app and site can violate app store guidelines. Companies are not usually allowed to use push notifications for advertising content unrelated to the app itself. This can get your app removed from the store and can also damage user trust. Try other channels for this type of communication.
- Don’t forget to provide value: App publishers should treat the ability to communicate with users via push notifications as a privilege, not a right. They must provide value; if they don’t, push notifications will be ignored or turned off. Some users will uninstall the app altogether.
Strategy
Analytics and measurement are important tools for improving your app’s performance. How the push notifications are written is also important. To drive action, they need to convey value. Messaging strategies and tactics need to be measured and tested. Strategies such as maximizing opt-in rates, ensuring new users are properly onboarded and reducing app user churn rates are all key to an app’s success.
Other strategies include:
- Matching up each user’s data across channels (web, mobile, store etc.) to better understand user behavior.
- Encouraging users to opt in by offering them incentives and examples of the value your notifications will provide.
- Optimizing the app experience to keep customers engaged.
Get Professional Help With Your Push Infrastructure
Push notifications can be targeted to segments of your user base and even personalized for specific app users. However, they also require careful management of user identification data and an interface for writing, targeting and sending messages. For this reason, building and maintaining a cross-platform push notification service takes significant resources and ongoing maintenance, including yearly updates for any relevant changes from the OS.
Publishers can build this infrastructure themselves or hire a vendor, such as Airship, to provide it. We provide capabilities such as:
- Reporting
- Scheduling
- Mobile marketing automation
- User attribute collection and segmentation
- Data management
- Security
- Cross-platform support
Increasingly, app publishers pay for push instead of building it so that they can focus on building better app experiences. If you want to learn more about how push notifications can help you connect with customers at each stage of the customer app lifecycle, contact us today, and let’s talk!
Other Frequently Asked Questions
Still have questions? See if we can answer any of them in the sections below.
What is the average click-through rate for push notifications compared to emails?
Click rates for push depend heavily on the message content, the industry, and how engaged the audience is. Typically, however, push notifications have a much higher click rate than emails, as they’re shorter, instant and get direct interaction from the lock screen or Notification Center. They’re also not impacted by spam filters. For these reasons, emails have a 1-2% click rate, while push notifications have an average of around 3%.
How is the effectiveness of a push notification measured?
Common metrics used to measure the efficacy of push notifications include open, click-through (CTR), conversion, and retention rates. You can also use your platform’s analytics tools to track how individual notifications perform against your internal success metrics.
What happens with push notifications when a device is offline?
If a user’s phone goes offline, the notification you send will be delivered as soon as the person has reconnected to the internet. This ensures people don’t miss any important alerts when they’re offline. However, it does interfere with the timing of the notifications.
Can push notifications incorporate multimedia content?
These types of push notifications are called “rich notifications”. On iOS, they can include videos, GIFs, images and even sound bites. Android only supports static images like JPG and PNG. When used appropriately, they tend to be more engaging and give users a better experience.
Are push notifications compliant with data protection regulations like GDPR?
The EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requires user education on how their data is used and collected. Sending them notifications requires their consent, and app developers need to ensure their push notifications are compliant with these requirements. You can comply with them by checking the rules on the GDPR’s website and giving users the option to consent and opt-out.
Can push notifications be scheduled?
Yes! You can schedule notifications ahead of time to be delivered on a predetermined date and time when you know users are most active. If you aren’t sure when this is, you can test sending notifications at scattered times throughout the day and see which time of day has the best open rate.
What’s the difference between a mobile and web push notification?
The primary distinction is the location from which the notification is delivered. Mobile push notifications are sent from a native mobile app, while web push notifications are delivered with web browsers. Mobile push notifications require a mobile app, but web push notifications can be used on both web browsers and mobile devices.